Coeliac disease is an autoimmune condition that affects the digestive system. It triggers an adverse reaction to gluten, a protein found in foods like wheat, oats, barley, and rye. When someone with coeliac disease consumes gluten, their immune system attacks the lining of the small intestine. This can lead to a variety of digestive and general health symptoms. While the digestive effects of coeliac disease are well known, less information is available on how this condition may impact areas such as fertility and pregnancy.
This article discusses how coeliac disease can affect fertility, the risks associated during pregnancy, and what women with coeliac disease can do to ensure a healthy pregnancy. We will explore key aspects for those seeking to understand the connection between coeliac disease and pregnancy, answering common questions and offering practical advice.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is coeliac disease and how does it relate to fertility?
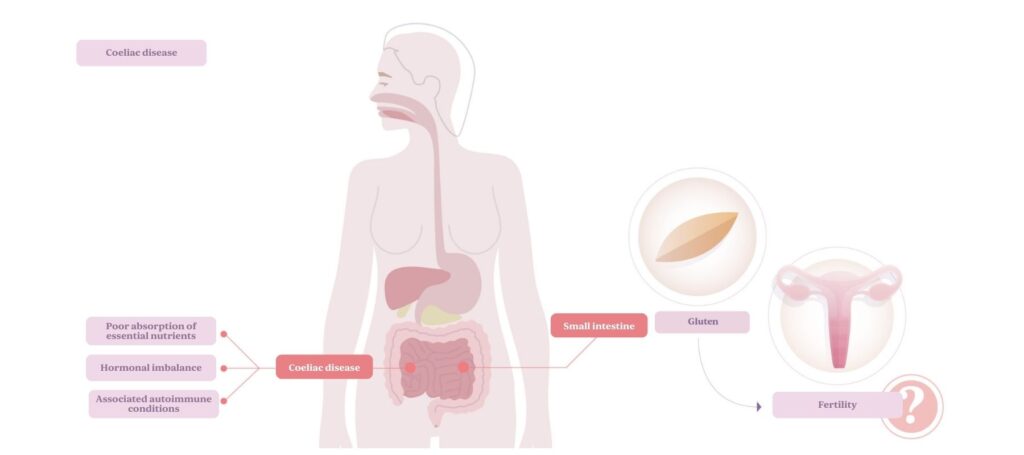
Coeliac disease affects approximately 1% of the global population. The condition can have a significant impact on reproductive health, particularly in women of childbearing age. Various studies have shown that women with undiagnosed or inadequately treated coeliac disease may experience difficulties conceiving.
This is due to several factors:
- Malabsorption of essential nutrients: Coeliac disease damages the small intestine and affects the absorption of crucial nutrients such as iron, folic acid, vitamin B12, zinc, and calcium. Deficiencies in these nutrients can negatively affect reproductive health and the ability to maintain a healthy pregnancy.
- Hormonal imbalance: Chronic inflammation caused by gluten in coeliac individuals can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting menstrual cycles and ovulation. This may result in irregular periods and even fertility problems.
- Associated autoimmune conditions: Coeliac disease is associated with other autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, which may also affect fertility.
Can coeliac disease cause infertility?
Not everyone with coeliac disease experiences infertility. However, studies have found that untreated coeliac disease can double the risk of infertility in both men and women. It is important to note that, in most cases, adopting a gluten-free diet under medical supervision can help restore fertility.
In many cases, once coeliac individuals begin to avoid gluten and achieve better nutrient absorption, their fertility may significantly improve. Some studies even suggest that fertility in women with treated coeliac disease is similar to those without the condition.
Coeliac disease and pregnancy: associated risks
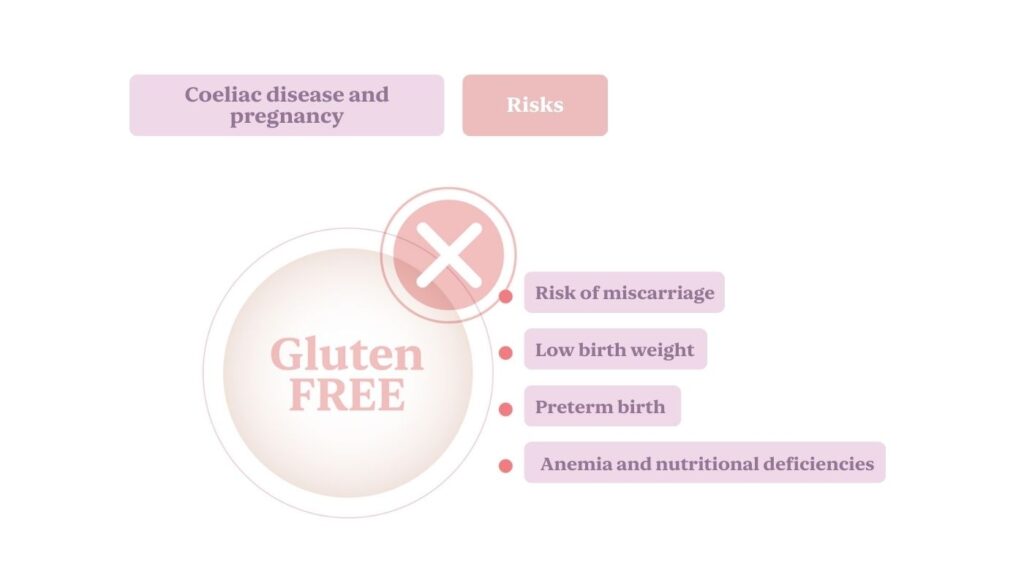
Once a woman with coeliac disease becomes pregnant, it is essential to maintain a strict gluten-free diet to avoid complications during pregnancy. Below are some risks related to untreated coeliac disease during pregnancy:
- Risk of miscarriage: Women with untreated coeliac disease have a slightly higher risk of miscarrying. This may be due to nutrient deficiencies that affect the formation and development of the fetus.
- Low birth weight: Malabsorption of nutrients can affect fetal growth, leading to an increased risk of low birth weight. This risk can be significantly reduced with an appropriate diet.
- Premature birth: Untreated coeliac disease has also been associated with a higher likelihood of preterm birth, which can lead to additional complications for the baby.
- Anemia and nutritional deficiencies: Anemia and other deficiencies can jeopardize the health of both mother and baby, affecting fetal development.
How to manage coeliac disease during pregnancy?
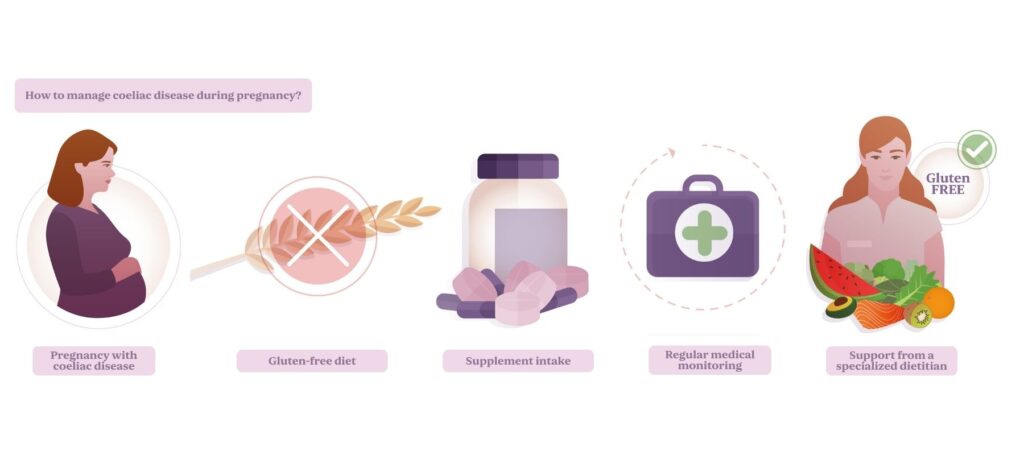
If a pregnant woman has coeliac disease, it is essential to follow certain steps to reduce risks:
- Adopt a gluten-free diet: It is vital to eliminate gluten entirely from the diet. This not only improves nutrient absorption but also helps reduce inflammation and prevents the onset of coeliac symptoms.
- Consume supplements: For many women with coeliac disease, taking iron, folic acid, vitamin D, and other supplements is essential, as their reserves may be compromised. Consulting with a nutritionist or treating doctor is crucial to personalize these supplements.
- Constant medical monitoring: During pregnancy, regular check-ups with a doctor familiar with the challenges of coeliac disease are crucial. Blood tests, ultrasounds, and other screenings will help monitor the health of both mother and baby.
- Support from a specialized dietitian: A dietitian with experience in coeliac disease can be extremely helpful in planning nutritious, balanced meals and ensuring adequate nutrient intake.
Coeliac disease and breastfeeding
The relationship between coeliac disease and breastfeeding is not as direct as the one between coeliac disease and pregnancy. However, it is important to note that maintaining a gluten-free diet during breastfeeding is also crucial. This helps prevent disease symptoms in the mother and ensures better milk quality.
Additionally, some studies suggest that breastfeeding may have a protective effect against coeliac disease in infants, especially if the mother avoids gluten. However, further research is needed to fully understand this relationship.
Frequently asked questions about coeliac disease and pregnancy
Is it safe to get pregnant if I have coeliac disease?
Yes, it is possible to have a safe and healthy pregnancy with coeliac disease, as long as appropriate recommendations are followed, such as maintaining a gluten-free diet and receiving the necessary nutrients.
Should I inform my gynecologist about my coeliac disease?
Definitely. It is essential that your gynecologist and medical team are aware of your condition so they can provide proper monitoring and perform necessary tests.
Will my baby have coeliac disease?
Coeliac disease has a genetic component, so if one or both parents have the condition, the baby has a higher risk of developing it. However, not all children of coeliac parents will develop the disease.
Conclusion: Caring for coeliac disease for a healthy pregnancy
Coeliac disease does not have to be an insurmountable obstacle for those wishing to start a family. While there are risks and challenges, a strict gluten-free diet and adequate medical supervision can help minimize the effects of the disease on fertility and pregnancy. For women with coeliac disease, staying informed and following medical recommendations are the best steps to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Remember that each case is unique. If you have coeliac disease and are considering pregnancy, it is best to consult with a maternal health specialist and a dietitian specialized in coeliac disease for personalized guidance. This way, you can ensure both your well-being and your future baby’s health.
Authors: