Table of Contents
Toggle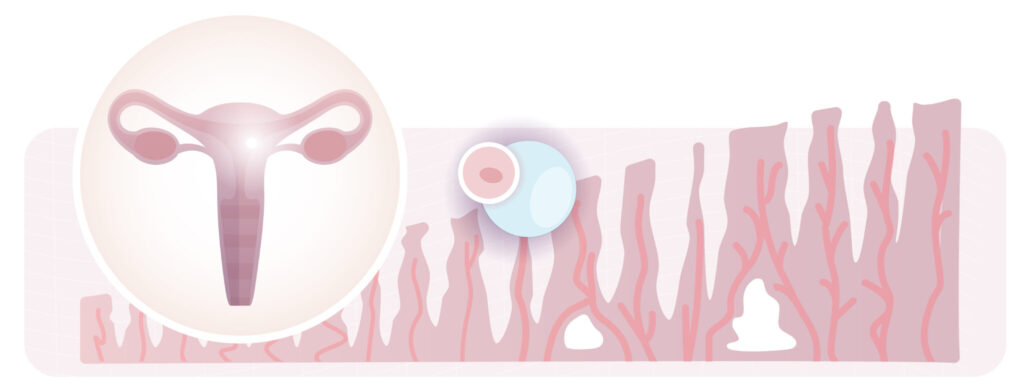
One of the first steps in pregnancy is embryo implantation, where the embryo attaches to the endometrium. Successful implantation is essential for pregnancy to continue. Three main conditions must be met: the endometrium must be receptive, the embryo must be healthy and at the blastocyst stage, and there must be proper molecular communication between the embryo and the endometrial lining.
What is embryo implantation?
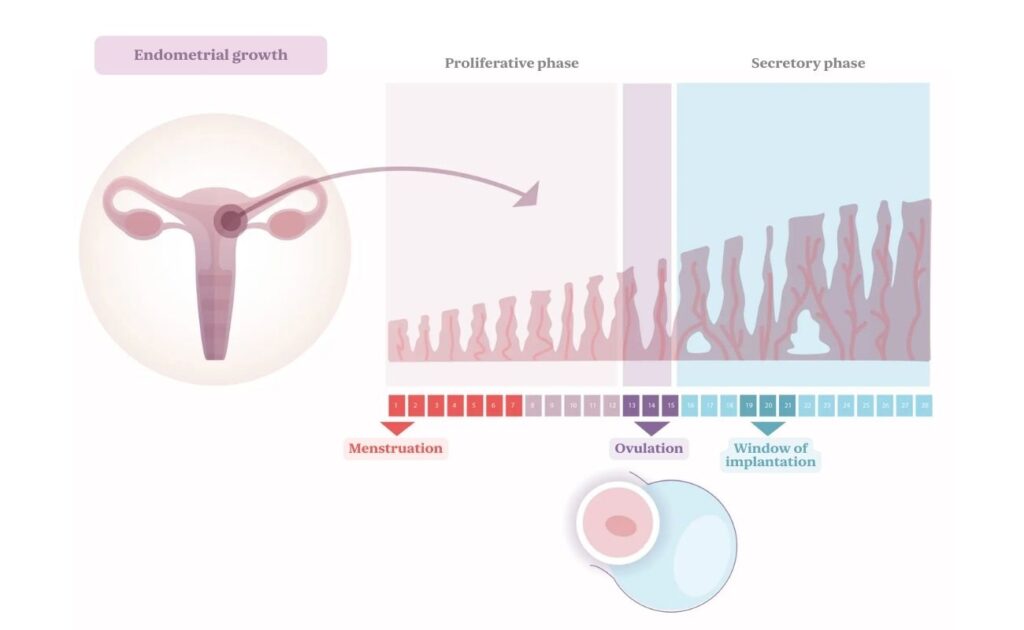
Embryo implantation is the process by which a blastocyst-stage embryo (about 5-6 days after fertilization) adheres to the endometrium, initiating pregnancy. After implantation, the embryo begins to develop along with supporting structures like the placenta and yolk sac. For the embryo to implant, the uterine lining must be at the ideal thickness and structure, generally between 7 and 10 millimeters. When these conditions are met, the endometrium is considered receptive.
When does embryo implantation occur?
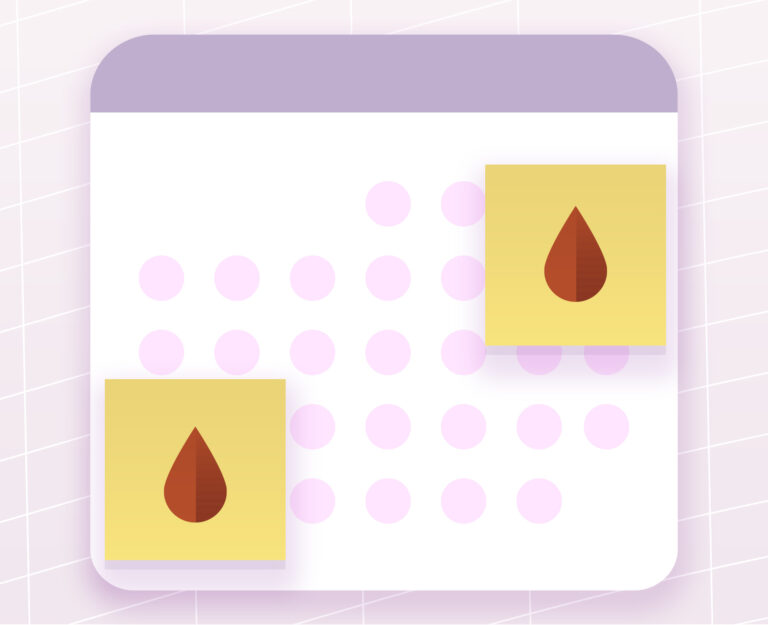
Just as there are fertile days ideal for conception, there is also a “window of implantation” during which the endometrium is most receptive. In a regular cycle, this occurs around days 19–21 after the start of menstruation. Implantation typically takes place 7–8 days after fertilization. Some women may experience implantation bleeding, though it is not always present and does not indicate failed implantation.
How can I support embryo implantation?
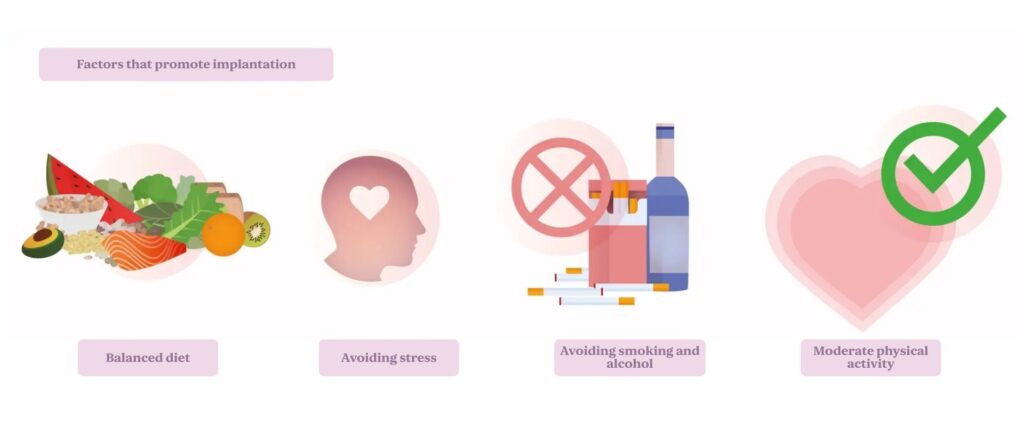
While some implantation factors are beyond our control, there are several habits and actions that can help support this crucial stage.
Avoid smoking and alcohol
These substances affect blood vessels and can reduce the likelihood of successful implantation and fertility in general.
Maintain a balanced diet
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Nutrients and antioxidants like vitamins C and E can support fertility.
Manage stress
Stress increases cortisol, which can interfere with ovulation and reduce the chances of implantation. Find tools and strategies to reduce stress, especially during fertility treatments.
Engage in moderate physical activity
Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga are ideal. Avoid high-intensity workouts that may cause physical stress. Light exercise supports circulation and general well-being, which helps create a healthy uterine environment.
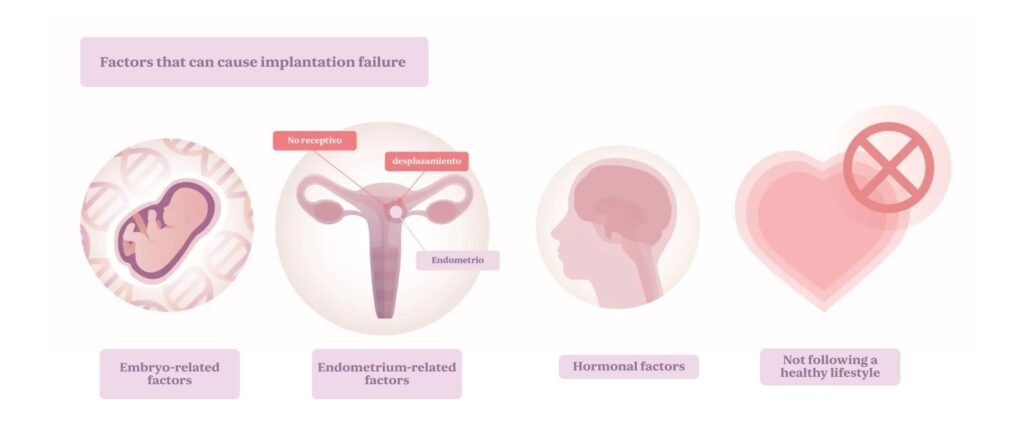
What causes implantation failure?
Implantation may occasionally fail due to several reasons related to the embryo, the uterine environment, or general health conditions.
Embryo-related factors
Genetic or chromosomal abnormalities may lower implantation chances. Low embryo quality or failure to reach the blastocyst stage can also play a role.
Endometrial factors
The window of implantation may shift, making the endometrium non-receptive at the critical time. Conditions like endometriosis, polyps, fibroids, or other abnormalities can interfere with implantation.
Hormonal factors
Hormones like estrogen and progesterone prepare the endometrium. Hormonal imbalances can negatively impact implantation potential.
Unhealthy lifestyle
Alcohol, tobacco, poor nutrition, and chronic stress can affect implantation. Identifying and addressing these issues can improve success rates.
Authors: