Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, affecting various body functions, including the reproductive system. Many women wonder if pregnancy with hypothyroidism is possible or if this condition may hinder conception. The answer is yes, it is possible to get pregnant with hypothyroidism, as long as the condition is well controlled. Achieving this requires hormone levels—especially thyroid hormones—to be within the recommended range to support conception.
This article explores how hypothyroidism can affect fertility, the ideal hormone levels to conceive, and what you can do to improve your chances of getting pregnant with this condition.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow does hypothyroidism affect fertility?
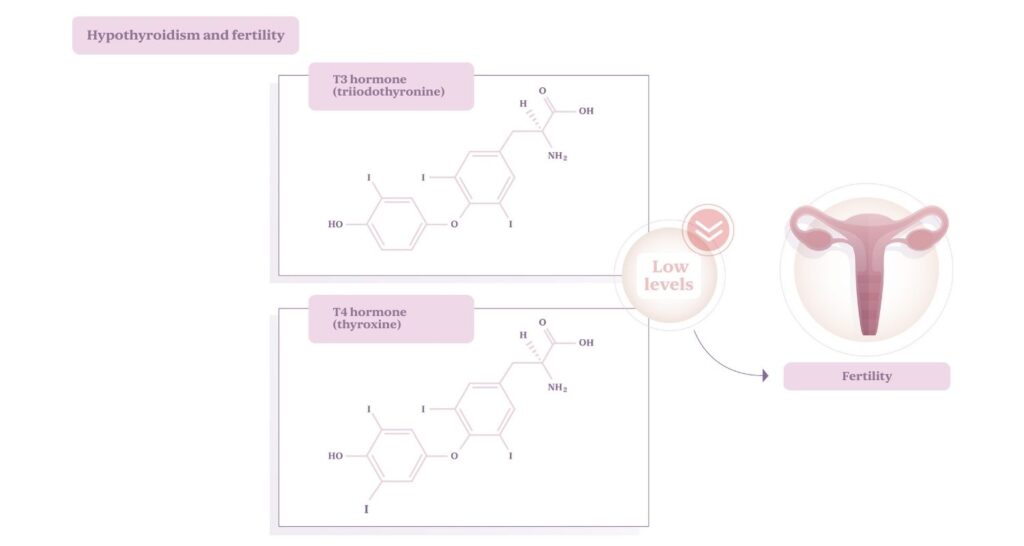
The thyroid plays a crucial role in metabolism and regulates various body functions, including those that influence the menstrual cycle and ovulation. Thyroid hormones, T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), are essential for proper ovarian function and the production of sex hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, which are vital for ovulation and pregnancy.
Low levels of these hormones, as seen in hypothyroidism, can disrupt the menstrual cycle and interfere with regular ovulation. Without ovulation, the chances of pregnancy decrease. Additionally, hypothyroidism can affect egg quality and increase the risk of miscarriage and pregnancy complications.
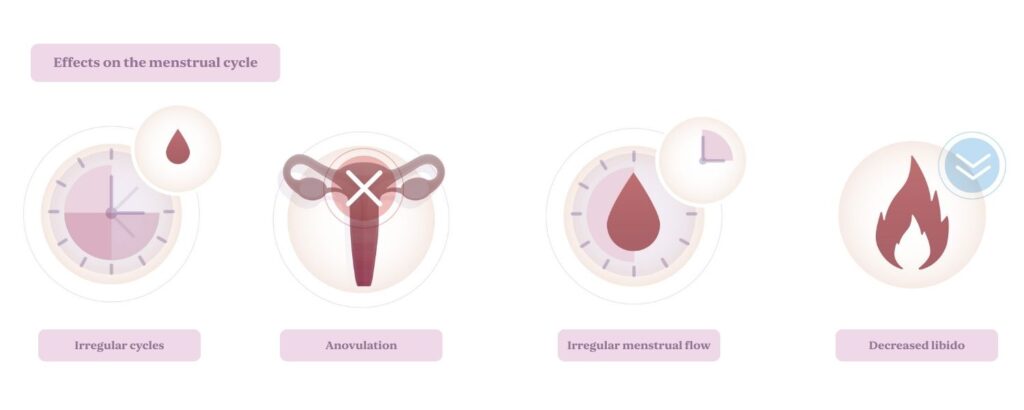
Effects of hypothyroidism on the menstrual cycle:
- Irregular cycles: Hypothyroidism can cause longer or shorter menstrual cycles, making it difficult to predict ovulation.
- Anovulation: Poorly controlled hypothyroidism can prevent ovulation from occurring.
- Abnormal menstrual bleeding: Women with hypothyroidism may experience heavy periods or, conversely, absent periods (amenorrhea).
- Decreased libido: Low thyroid hormone levels can reduce sexual desire, indirectly affecting the chances of conception.
Can you get pregnant with hypothyroidism?
Yes, it is possible. The key is to keep hypothyroidism properly managed through appropriate medical treatment and regular monitoring of hormone levels. Thyroid hormone levels must remain within optimal ranges to support regular menstrual cycles and healthy ovulation. If these values are not well controlled, conceiving can become more difficult.
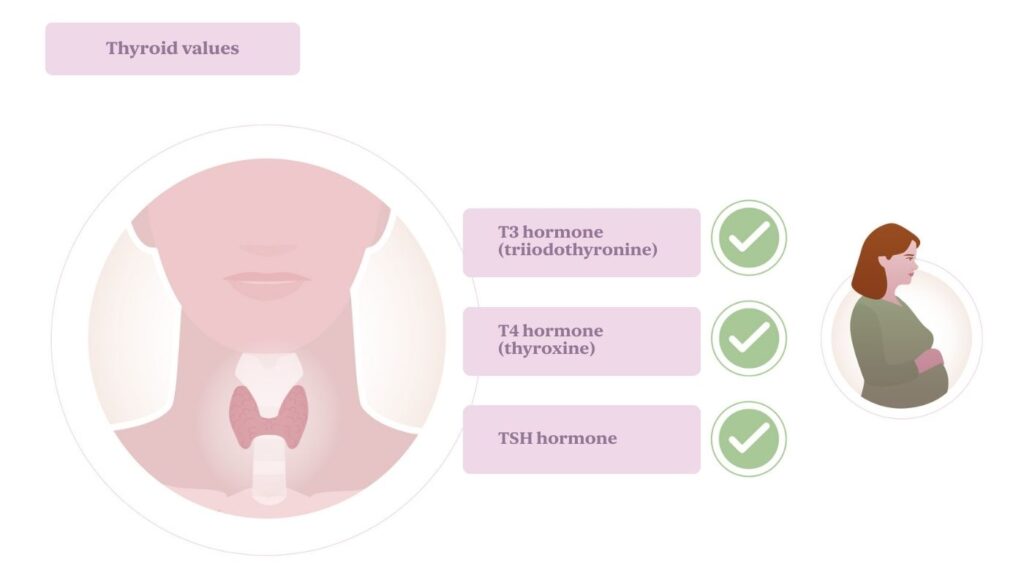
Optimal thyroid levels for conception
It is particularly important to monitor the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free T4, and in some cases, T3. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland and regulates the production of thyroid hormones. The recommended TSH levels for women trying to conceive are stricter than for the general population.
The optimal TSH range for women seeking pregnancy should be between 0.5 and 2.5 mIU/L. Maintaining this range helps ensure proper thyroid function, supporting regular cycles and ovulation.
It is important to note that these recommended values for women trying to conceive are stricter than those considered normal for the general population, which can go up to 4.5 mIU/L. Hormonal balance is crucial to achieving and maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
Hypothyroidism treatment while trying to conceive
The standard treatment for hypothyroidism is levothyroxine, a synthetic version of the T4 hormone. Your endocrinologist will adjust the dosage according to your TSH levels to keep them within the recommended range. Continuous monitoring with an endocrinologist or fertility gynecologist is essential when trying to conceive and throughout pregnancy to make any necessary treatment adjustments.
Subclinical hypothyroidism and pregnancy
Subclinical hypothyroidism is a mild form of the condition in which TSH levels are elevated but T3 and T4 remain within normal limits. Even though it may not cause obvious symptoms, subclinical hypothyroidism can still impact fertility and increase the risk of pregnancy complications.
It is recommended to undergo thyroid function tests before attempting to conceive, even if you don’t present symptoms, as subclinical hypothyroidism can go unnoticed.
Pregnancy complications with hypothyroidism
Proper control of hypothyroidism during pregnancy is essential. Poorly managed thyroid levels can lead to serious complications such as:
- Miscarriage: High TSH or low thyroid hormone levels may increase the risk of pregnancy loss.
- Preterm birth: Women with hypothyroidism are at higher risk of delivering before 37 weeks of gestation.
- Preeclampsia: This condition causes high blood pressure and can be dangerous for both the mother and baby.
- Low birth weight: Maternal hypothyroidism may affect fetal growth, resulting in a baby with low birth weight.
- Neurodevelopmental issues: Thyroid hormones are critical for the baby’s brain development, especially in the first trimester. Poorly controlled hypothyroidism may impact the child’s cognitive development.
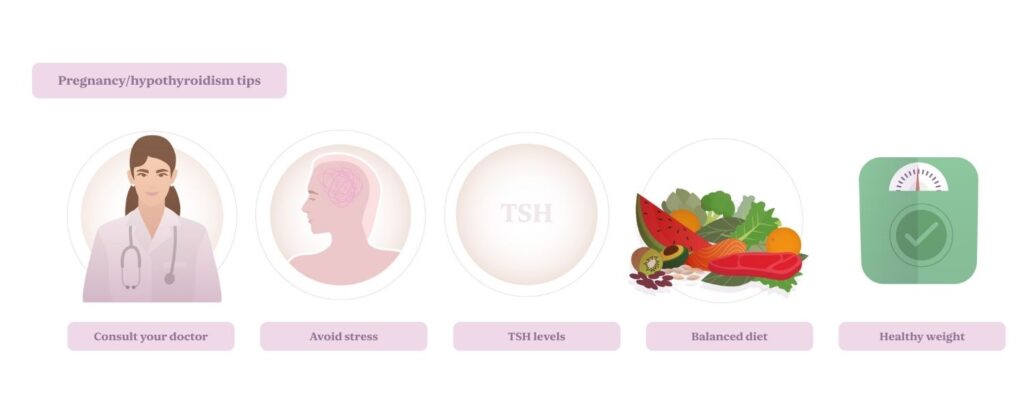
Tips for getting pregnant with hypothyroidism
If you have hypothyroidism and are planning to get pregnant, follow these tips to improve your chances of conception and support a healthy pregnancy:
- Consult your doctor: Make sure your hypothyroidism is well-controlled before trying to conceive. Talk to your endocrinologist or gynecologist about your pregnancy plans.
- Monitor your TSH levels: Throughout the conception journey and during pregnancy, your doctor should adjust the levothyroxine dosage based on your TSH levels.
- Maintain a balanced diet: A healthy diet rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc can support optimal thyroid function.
- Reduce stress: Chronic stress can impact both fertility and thyroid function. Try to incorporate relaxation techniques into your daily routine.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or underweight can affect hormonal balance, so maintaining a healthy weight can improve your chances of conceiving.
Why see a fertility specialist
If you have hypothyroidism and are struggling to conceive, it’s advisable to consult a fertility specialist. A fertility gynecologist can help identify any additional factors affecting your ability to get pregnant and offer treatment options or additional support if necessary.
A specialist will also ensure that your thyroid function is optimally controlled, adjust treatments as needed, and help manage any fertility or pregnancy-related complications. In addition, they provide emotional support and guidance throughout your fertility journey. If you need personalized advice, you can book an appointment with no obligation.
Conclusion
While hypothyroidism can affect fertility, it does not prevent women from becoming pregnant when properly managed. The most important thing is to maintain medical control of the condition and ensure hormone levels stay within the recommended range. With the right treatment and regular follow-up, many women achieve pregnancy with hypothyroidism and enjoy a healthy pregnancy.
If you have questions or are experiencing difficulty conceiving, remember that you can always consult a fertility specialist for personalized guidance. Your health and well-being come first!